how to disable laptop wifi card

Title: How to enable or disable Wi-Fi and Ethernet network adapters on Windows 10
Channel: Computer Everywhere
How to enable or disable Wi-Fi and Ethernet network adapters on Windows 10 by Computer Everywhere
how to disable laptop wifi adapter, how to enable laptop wifi adapter, disable wifi on laptop, disable wifi card in bios, how to disable wifi card
Laptop WiFi Dying? KILL It (Without Losing Your Mind!)
Is Your Laptop's WiFi a Digital Disaster? Here's How to Conquer It!
Let’s face it. A sputtering, unreliable WiFi connection is the bane of the modern existence. It's almost as frustrating as a low battery. Your laptop feels like a digital anchor, dragging you down. That moment when you need the internet most the WiFi decides to take a nap. So, what to do? Don't panic. We'll dissect the common culprits and revive your connection. You can regain your digital freedom.
Cracking the Code: Unmasking the WiFi Villain
Before you smash your laptop (tempting, I know!), let’s identify the enemy. WiFi problems aren't always what they seem. First, check the obvious. Is your router powered on? Is the power cord plugged in securely? Sometimes, the simplest solutions are the most effective. Afterward, consider the placement of your router. Walls, furniture, and even other electronics can interfere with the signal. Therefore, move your router to a more central, open location. This can significantly improve your connection.
Signal Strength Secrets: Boosting Your WiFi Reach
A weak signal is a common issue. Because your router is distant, your laptop may struggle to connect. Consequently, you should try these methods. First, restart your router and modem. This simple step resolves many temporary glitches. Also, update your router's firmware. Manufacturers regularly release updates to improve performance. Additionally, try moving closer to the router as a quick test. If that works, invest in a WiFi extender. This helps to amplify the signal throughout your home.
The Router Renegade: Troubleshooting Your Network's Heart
Your router is the heart of your home network. Moreover, it can sometimes develop hiccups. First, access your router's settings. This is often done by entering the IP address (usually 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1) in your web browser. Then, check for any error messages or unusual activity. After that, look for devices connected to your network. Are there any unknown devices using your bandwidth? If so, you might need to secure your network with a strong password. Further, consider changing your WiFi channel. Many routers automatically select a channel. However, this channel might be congested. Experiment with different channels in your router settings. This will find a better channel.
Laptop's Lost Connection: Isolating the Internal Culprit
Sometimes, the problem isn't the router. It’s often the laptop itself. First, ensure your WiFi adapter is enabled. Check your system's settings. This often involves clicking on the WiFi icon in your system tray. Second, update your network adapter driver. Outdated drivers can cause compatibility issues. Go to Device Manager, locate your network adapter, and update the driver. Furthermore, run the Windows Network Troubleshooter. Windows has built-in tools for diagnosing and fixing network problems. It will often provide helpful suggestions.
Beware of Bandwidth Bandits: Minimizing Interference
Several factors can interrupt your WiFi signal. Devices like microwaves and Bluetooth gadgets can cause interference. So, try to minimize these disruptions. Moreover, limit the number of devices using the WiFi simultaneously. Streaming video on multiple devices can drain your bandwidth. Consequently, prioritize your most important tasks. Therefore, consider temporarily disconnecting other devices. This lets your laptop have more bandwidth.
Security Safeguards: Protecting Your Connection
Protecting your WiFi is crucial. A compromised network can expose your data. First, ensure your router uses a strong password. Change the default password. Also, enable WPA2 or WPA3 encryption. This is the current standard in security. Moreover, update your router's firmware regularly. Patches often address security vulnerabilities.
The Ultimate WiFi Recovery Checklist: A Quick Recap
Let’s summarize the key steps. First, restart your router and modem. Next, check your router's placement. Afterward, update your firmware and drivers. Then, run the Windows Network Troubleshooter. Subsequently, limit interference. Finally, secure your network. These steps are your defense against a failing WiFi connection.
When All Else Fails: Seeking Expert Assistance
If you have tried everything, and nothing works, don't despair. Contact your internet service provider (ISP). They can check for any problems on their end of the connection. Otherwise, consider consulting a computer technician. They're specialists in network problems. They can provide advanced diagnostics and repairs. They can restore your peace of mind.
The Bottom Line: Reclaiming Your Digital World
A flaky WiFi connection is beyond annoying. It is a disruption. However, with a little troubleshooting, you can often fix it. You can restore your online access. So, use these steps and take control of your digital world. You can conquer those connectivity frustrations. It is possible to enjoy seamless internet access once again. Now, go forth and browse! Your digital life awaits!
Laptop WiFi Nightmare? FIX This NOW!Laptop WiFi Dying? KILL It (Without Losing Your Mind!)
Alright, let’s be real. There's nothing quite as infuriating as your laptop's Wi-Fi dropping out mid-Zoom call, right when you're about to deliver that killer presentation. Or, even worse, when you're in the thick of a Netflix binge and the buffering wheel of doom decides to make a guest appearance. We’ve all been there. That slow, agonizing crawl of the download bar. The blank screen that taunts you with its emptiness. It’s enough to make you want to chuck your precious piece of technology out the window (we wouldn't recommend that, by the way!). But before you resort to drastic measures, let's talk about fixing that flaky Wi-Fi. We’re going to troubleshoot this, and get your laptop back to its connectivity best, all without turning you into a tech-induced rage monster. Think of this as your survival guide, your digital defibrillator, if you will, for a dying wireless connection.
1. The Silent Killer: Why Is Your Laptop's Wi-Fi Suddenly Giving Up the Ghost?
Before we start wielding virtual screwdrivers, we need to understand the enemy. Why is your Wi-Fi being such a drama llama? The reasons are as varied as the breeds of cats that probably spend their lives perched atop your router. Sometimes, it's a simple glitch. Other times, it's a rogue program, a faulty driver, or even your router itself throwing a tantrum. We can break this down into a few key areas:
- Software Shenanigans: Corrupted drivers, conflicting software, or even a simple operating system update gone wrong can all wreak havoc on your Wi-Fi adapter. Imagine your drivers as the translators between your laptop and the internet; if they're speaking gibberish, nobody understands anyone.
- Hardware Hiccups: Your Wi-Fi adapter, the little chip that does all the wireless magic, can malfunction. It could be a loose connection, overheating, or just plain old hardware fatigue. It’s like your laptop’s brain losing its ability to process the internet.
- Router Rumble: Your router is the gatekeeper to the internet. If it's having issues, your Wi-Fi is going to suffer, like a traffic jam causing delays everywhere. Think of it as the grumpy bouncer at the internet club – if he's not feeling friendly, nobody gets in.
- Environmental Enemies: Walls, microwaves, Bluetooth devices, and even other Wi-Fi networks can interfere with your signal. Imagine trying to have a conversation at a rock concert; it's the same kind of struggle.
2. The First Responder: Basic Troubleshooting Steps (Don't Panic!)
Okay, deep breaths. Before you go tearing your hair out, let’s try some simple fixes. These are the equivalent of calling 911 for your Wi-Fi – quick and easy.
- The Classic Restart: We laugh, but it works! Restarting your laptop and your router can often clear up temporary glitches. It’s like hitting the reset button and giving everything a fresh start. Turn them both off, wait a minute or two, and then power them back up.
- Airplane Mode Tango: Toggle airplane mode on and off. This forces your Wi-Fi adapter to reset. It's a bit like giving your Wi-Fi a mini-reboot.
- Check the Obvious: Ensure your Wi-Fi is actually on. Sounds silly, but we’ve all done it. Also, double-check the Wi-Fi icon in your system tray to make sure it's not showing a "no connection" message.
- Look for Interference: Move your laptop closer to the router and see if that improves the signal. Be mindful of other electronic devices around you.
3. Driver Dilemmas: Updating and Reinstalling Your Wi-Fi Driver
Drivers are crucial! They tell your laptop how to talk to your Wi-Fi adapter. Outdated or corrupted drivers are a common cause of Wi-Fi woes.
- Update Your Driver:
- Go to Device Manager (search for it in the Windows search bar).
- Expand "Network Adapters."
- Right-click on your Wi-Fi adapter (it will have a name like "Intel Wireless-AC" or "Qualcomm Atheros").
- Select "Update driver." Choose "Search automatically for drivers."
- Reinstall Your Driver (If Updating Doesn't Work):
- In Device Manager, right-click on your Wi-Fi adapter and select "Uninstall device."
- Restart your laptop. Windows should automatically reinstall the driver, hopefully fixing the problem.
4. Router Resurrection: Checking and Resetting Your Router
Your router is the central hub, so it needs to be working properly.
- Router Reboot: Turn off your router and unplug it from the power source for at least 30 seconds. Plug it back in and wait for it to fully boot up.
- Firmware Update: Outdated router firmware can cause performance issues. Access your router's settings (usually by typing its IP address into your web browser) and look for a firmware update option.
- Factory Reset (Last Resort): If everything else fails, you can reset your router to its factory settings. Be warned: this will erase your custom settings, like your Wi-Fi password, so have that information handy! Usually, there’s a small reset button on the back of the router that you can press with a paperclip.
5. Signal Strength Showdown: Optimizing Your Wi-Fi Setup
Is your Wi-Fi signal strong enough to reach your laptop? It's like trying to have a phone conversation with someone who's whispering across a football field.
- Router Location: Place your router in a central location, away from walls and obstructions. Elevated positions are often best.
- Channel Changing: Your router broadcasts on a specific channel. Other Wi-Fi networks can interfere. Access your router settings and try switching to a less congested channel (often channels 1, 6, and 11 are recommended).
- Antenna Angles: Experiment with the position of your router's antennas. Sometimes a slight adjustment can make a big difference.
6. The Spy Within: Running a Network Troubleshooter
Windows has a built-in network troubleshooter that can diagnose and fix many Wi-Fi problems automatically. Think of it as a digital detective.
- Type "Troubleshoot settings" into the Windows search bar and open it.
- Click on "Network and Internet."
- Click "Wi-Fi" and then "Run the troubleshooter."
- Follow the on-screen instructions. This will often identify simple problems, like a disconnected network cable or a faulty network setting.
7. The Malware Menace: Scanning for Infections
Sometimes, malware can interfere with your network connections.
- Run a full scan with your antivirus software. Ensure your software is up to date.
- Consider running a malware scanner like Malwarebytes, which can often find threats that your antivirus might miss.
8. Power Saving Perils: Disabling Power Management for WiFi
Windows, by default, sometimes limits the power to your Wi-Fi adapter to save battery life. This can cause connection issues.
- Go to Device Manager (as described above).
- Right-click on your Wi-Fi adapter and select "Properties."
- Go to the "Power Management" tab.
- Uncheck the box that says "Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power."
9. Clean Up the Clutter: Removing Unnecessary Software and Programs
Too many programs running in the background can hog your resources and slow down your Wi-Fi.
- Close unnecessary programs running in the system tray (the area with icons in the bottom right corner of your screen).
- Disable startup programs that you don't need. Go to Task Manager (right-click on the taskbar and select it), and then go to the "Startup" tab. Disable programs that automatically start when your computer boots up.
10. The Bandwidth Breakdown: Checking Your Internet Speed
Sometimes, your Wi-Fi isn't the problem; your internet connection is just slow.
- Run a speed test at a site like Speedtest.net.
- Compare your results to the speed you're paying for from your internet service provider (ISP).
- If your speeds are consistently slow, contact your ISP.
11. Hardware Heroes: Evaluating Your Wi-Fi Adapter (Is It Dying?)
If all else fails, it could be a problem with your Wi-Fi adapter itself.
- External USB Wi-Fi Adapter: These are inexpensive and easy to use. You can plug one in and test if it resolves your problems. If it does, your built-in adapter may be the culprit.
- Internal Adapter Replacement: If you're comfortable with opening up your laptop, you can replace the internal Wi-Fi adapter. (Always disconnect the power supply before opening your laptop). This is more advanced, and you should consult your laptop's service manual.
12. Firewall Fury: Checking Your Firewall Settings
Your firewall can sometimes block your Wi-Fi connection.
- Make sure your firewall isn't blocking your Wi-Fi adapter.
- You can temporarily
Wi-Fi automatically disconnecting problem solved wifiproblem laptop viral shorts

By THE TECH INDIA Wi-Fi automatically disconnecting problem solved wifiproblem laptop viral shorts by THE TECH INDIA
How To Fix Wireless Adapter Missing In Windows 10 Get WiFi Adapter Back
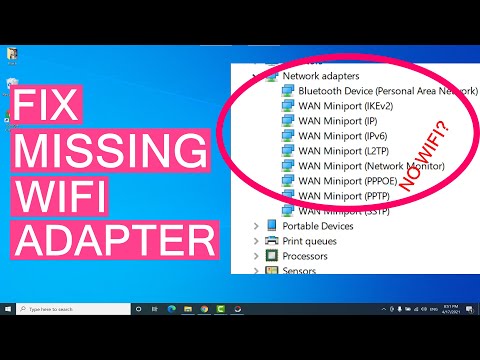
By Sandeep Singh How To Fix Wireless Adapter Missing In Windows 10 Get WiFi Adapter Back by Sandeep Singh
How to solve Wi-Fi Not showing Problem in Windows 10 200 Fixed

By Rounak Verma How to solve Wi-Fi Not showing Problem in Windows 10 200 Fixed by Rounak Verma

Title: How to disable internal wifi of a laptop
Channel: Wide Spectrum
How to disable internal wifi of a laptop by Wide Spectrum
Change Wifi Settings
Laptop WiFi Dying? KILL It (Without Losing Your Mind!)
We've all been there. You're in the middle of an important video call, streaming your favorite show, or finally making progress on a crucial project, and bam! Your laptop's WiFi signal fades to black. The loading circle spins tauntingly. The frustration mounts. Before you launch your delicate device across the room, take a deep breath. This isn't necessarily a death sentence for your wireless adapter. Let’s troubleshoot and conquer your connectivity woes.
Recognizing the WiFi SOS: Pinpointing the Problem
The first step in slaying the WiFi gremlins is identifying the root cause. A dying WiFi connection can manifest in a multitude of ways, and understanding the specific symptoms is crucial for choosing the right weapon in your troubleshooting arsenal. Is your connection dropping intermittently, or is it consistently unreliable? Are you seeing a full signal strength indicator, but no internet access? Or is the signal strength itself weak and fluctuating?
- Intermittent Drop-Offs: These are the most common and often the trickiest. The internet works, then it doesn't, then it works again. This could point to a problem with your router, your internet service provider (ISP), or even interference from other devices.
- No Internet Access Despite Full Signal: This situation suggests your laptop is connecting to the WiFi, but it's not communicating effectively with the internet. This could be a problem with your router’s DHCP server, a conflict with your IP address, or even a DNS issue.
- Weak or Fluctuating Signal: This is the most straightforward. If the bars on your WiFi indicator are perpetually low or frequently changing, you’re likely experiencing signal strength problems. This could be due to distance from the router, physical obstructions, or interference.
- Slow Speeds All the Time: This could be a sign your speed is being throttled by your internet service provider. Contact your ISP to see if they can provide a higher speed.
Make a mental note of the exact symptoms you are experiencing. This will help pinpoint the cause.
The Basic First Aid Kit: Quick Fixes To Try Immediately
Before diving into more complex solutions, let’s start with the low-hanging fruit. These quick fixes often resolve the most common WiFi problems:
- The Reboot Ritual: Restarting your laptop and your router is often the first and most successful step. Turn off the router, wait 30 seconds, then turn it back on. Then, restart your laptop. This simple process clears temporary glitches in both devices.
- Moving Closer (or Reducing Obstacles): Physical distance and obstructions are WiFi’s enemies. Move your laptop closer to the router to improve signal strength. If there are obstacles such as thick walls or metal objects, try to reposition your laptop, or the router.
- Disable and Re-enable WiFi: On your laptop, turn the WiFi off, wait a few seconds, and then turn it back on. It's a digital reset that often fixes problems.
- Forget and Reconnect to the Network: Sometimes, cached network settings can cause issues. In your laptop's WiFi settings, "forget" the network you're trying to connect to, and then reconnect to it, re-entering the password.
- Check for Interference: Microwaves, cordless phones, and other electronic devices can interfere with your WiFi signal. Try to move your laptop away from these devices or turn them off temporarily to see if it improves your connection. If you have other devices such as baby monitors and bluetooth headphones, make sure it isn't interference creating an issue.
Deeper Dive: Troubleshooting Your Laptop's WiFi Adapter
If the basic fixes don't work, it's time to investigate your laptop's WiFi adapter itself. Windows and macOS both provide tools for diagnosing and troubleshooting network problems.
- Windows Network Troubleshooter: Windows has a built-in troubleshooter. Click the WiFi icon in your system tray (the area near the clock) and select "Troubleshoot problems." This tool can identify and automatically fix many common WiFi issues, such as problems with the network adapter drivers or incorrect network settings.
- Checking Device Manager (Windows): Open the Device Manager (search for it in the Windows search bar). Expand the "Network adapters" section. You should see your WiFi adapter listed (e.g., "Intel(R) Wireless-AC 9560").
- Driver Issues: Look for a yellow exclamation mark next to the adapter. This signifies a driver problem. Right-click on the adapter, select "Update driver," and follow the prompts. You can search automatically for updated drivers. If that doesn't work, you may need to download the latest WiFi adapter drivers from the manufacturer's website (e.g., Intel, Broadcom, etc.). Identify your laptop model and operating system.
- Disabled Adapter: If the adapter is disabled, right-click it and select "Enable device."
- Network Diagnostics (macOS): macOS has a built-in network diagnostics tool. Open "Network Utility" (search for it using Spotlight). Select the "WiFi" tab. The utility can provide diagnostic information about your WiFi connection and suggest solutions.
- Check the Hardware Switch: Some laptops have a physical switch (often on the side or front) that can disable the WiFi adapter. Make sure this switch is in the "on" position.
Router Revelation: Examining Your Home Network's Core
Your router is the heart of your home network, and a malfunctioning router can cause significant WiFi problems.
- Router Firmware Updates: Outdated firmware can lead to performance problems, security vulnerabilities, and compatibility issues. Access your router's administration panel (usually by typing its IP address into your web browser—check your router's manual or look for it online). Find the "Firmware Update" section and check for updates.
- Router Placement: As mentioned earlier, the physical location of your router is crucial. Position the router in a central location, away from walls, metal objects, and other sources of interference. Elevating the router also improves signal propagation.
- Channel Congestion: WiFi routers operate on different "channels". If your neighbors are using the same channel as you, it can cause interference and slow down your connection. You can use a WiFi analyzer app (available for both Windows and macOS) to identify the best channel for your router. Access the router's administration panel and change the WiFi channel if necessary. Channels 1, 6, and 11 are generally recommended.
- Router Overload: Does your router support the number of devices you have connected? If you have a lot of devices, consider upgrading to a router that can handle the load. Some routers have a device limit.
Advanced Arsenal: Deeper Troubleshooting Techniques
If the above steps haven’t solved the issue, it's time to move on to more advanced techniques.
- Renewing Your IP Address (Windows): Open the Command Prompt (search for it in the Windows search bar) and type the following commands, one at a time, pressing Enter after each:
ipconfig /releaseipconfig /renewipconfig /flushdnsThese commands force your computer to request a new IP address from your router, which can resolve IP address conflicts.
- Network Adapter Settings (Windows):
- Open the Device Manager (search for it in the Windows search bar) and expand the "Network adapters" section.
- Right-click your WiFi adapter and select "Properties."
- Click on the "Advanced" tab.
- Experiment with different settings, such as "Wireless Mode" (try different options like 802.11b/g/n/ac), and "Transmit Power." Make small adjustments one at a time, testing your connection after each change. Remember to write the settings down so that you can revert later if necessary.
- Run in Safe Mode with Networking: Starting your laptop in Safe Mode with Networking can help you determine if the problem is caused by a third-party driver or software. Hold down the Shift key when clicking the Restart button. This will open a recovery menu. Select Troubleshoot, then Advanced options, then Startup Settings and finally Restart. This will allow you to start your computer in Safe Mode. If the WiFi works in Safe Mode, it indicates that a third-party driver or software is the culprit.
- Factory Resetting Your Router: If all else fails, a factory reset might be necessary. This will erase all your custom settings, so make sure you know your internet connection type (e.g., PPPoE) and your ISP login information. Consult your router's manual for instructions on how to reset it. Be aware that you may have to set up the WiFi network.
When to Call for Reinforcements: Knowing When to Seek Professional Help
Sometimes, the problem is beyond your ability to fix it. Don't hesitate to call for professional help when:
- You've Tried Everything and Nothing Works: If you've exhausted all the troubleshooting steps and still can't connect, it’s time to call in the experts.
- Your Hardware Might Be Failing: If you suspect a hardware failure (e.g., a damaged WiFi adapter), it's best to seek professional repair.
- Your ISP is the Problem: If you suspect the issue is with
