internet doesnt connect with wifi in windows laptop

Title: 7 Ways to Fix a Computer That Can't Find or Connect to Wifi Windows 10 Laptops & Desktops
Channel: Ask A Computer Geek
7 Ways to Fix a Computer That Can't Find or Connect to Wifi Windows 10 Laptops & Desktops by Ask A Computer Geek
WiFi Nightmare on Windows? Fix Your Connection NOW!
WiFi Woes on Windows? Conquer Your Connection Conundrums!
Ever feel like your Windows PC is purposely sabotaging your Wi-Fi? It’s a frustrating experience. You’re ready to dive into work or stream your favorite show. Then, boom. No internet. Sound familiar? Well, you are not alone. Many Windows users face their own Wi-Fi nightmares. But don’t despair! Help is here.
The Dreaded Disconnect: Recognizing the Enemy
Let's be honest. A flaky Wi-Fi connection can test anyone's patience. Firstly, recognize the symptoms. Observe your computer's behavior. Does your signal strength fluctuate wildly? Does the connection drop unexpectedly? Do websites take an eternity to load? Perhaps you're receiving constant "limited connectivity" warnings. These are telltale signs. Therefore, identify these issues. They indicate a problem.
Troubleshooting Tactics: Your Wi-Fi Arsenal
Now, it's time to fight back! Before you chuck your computer out the window, attempt some simple fixes. Start with the basics. Restart your computer. Also, restart your router and modem. This step often solves the problem. Afterward, wait a few minutes. See if the connection improves. If it doesn't, proceed.
Driver Dilemmas: Updating the Secret Weapon
Drivers are crucial. They are the software that allows your computer to communicate. Outdated or corrupted drivers can cause havoc. Consequently, ensure your wireless adapter drivers are up-to-date. Here's how:
- Access Device Manager: Type "Device Manager" in the Windows search bar. Open it.
- Locate Network Adapters: Expand the "Network adapters" section. Find your wireless adapter (e.g., "Wi-Fi adapter").
- Update Driver: Right-click on your adapter. Select "Update driver". Choose "Search automatically for drivers." Windows will seek updates.
- Restart: After updating, restart your PC. This reboots the network settings.
In addition to updating drivers, consider uninstalling and reinstalling them. Sometimes, a fresh installation works wonders.
Network Reset: A Fresh Start for Your Connection
Sometimes, a more drastic approach is needed. Windows offers a network reset. It can resolve persistent connection problems. Keep in mind this will reset your network settings to their default. Here’s how to do it:
- Open Settings: Click the "Start" button. Then, go to "Settings".
- Network & Internet: Click on "Network & Internet".
- Advanced Network Settings: Scroll down. Select "Advanced network settings".
- Network Reset: Click on "Network reset". Follow the on-screen prompts.
After the reset, you'll need to re-enter your Wi-Fi password.
Investigating Interference: Unmasking the Hidden Culprits
Wi-Fi signals are vulnerable. They can be affected by interference. Several things can interfere with your Wi-Fi signal. This leads to slow speeds or dropouts. Consider potential sources of interference:
- Other Electronic Devices: Microwaves, Bluetooth devices, and cordless phones can cause problems.
- Physical Obstructions: Walls and metal objects can weaken the signal.
- Channel Congestion: Your router and others in your area may be using the same channel. This is often the cause of the problem.
Try moving your router. Experiment with different Wi-Fi channels. To discover the best channel, use a Wi-Fi analyzer app. These are available for both computers and smartphones.
Advanced Troubleshooting: Digging Deeper (If Necessary)
These steps often resolve most Wi-Fi issues. However, sometimes problems persist. Then, consider these further actions:
- Run the Network Troubleshooter: Windows has a built-in troubleshooter. It can automatically diagnose and fix common problems. Search for "Network troubleshooter" in the Windows search bar.
- Check Your Router Firmware: Make sure your router's firmware is up-to-date. Outdated firmware can cause stability issues. Check your router's manufacturer's website. Download the latest firmware, if available. Follow their instructions to update it.
- Consider Your Hardware: Is your Wi-Fi adapter old or damaged? A faulty adapter will hurt your connection. Consider replacing it if nothing else works.
Preventative Measures: Maintaining a Healthy Connection
Once you’ve fixed your connection, keep it working smoothly. Furthermore, adopt some preventative measures:
- Regular Driver Updates: Keep your drivers updated. Check for updates regularly.
- Secure Your Network: Use a strong password for your Wi-Fi network. Encrypt your network using WPA2 or WPA3 security.
- Router Placement: Place your router in a central location. Keep it away from interference sources.
- Restart Regularly: Restart your router and modem every few weeks. This helps maintain optimal performance.
Victory! Reclaiming Your Online Sanity
By following these steps, you should be free from Wi-Fi woes. Take back control of your connection. Now, enjoy smooth and reliable internet access! If all else fails, contact a qualified IT expert. They can help you troubleshoot in greater depth.
HP Laptop WiFi Nightmare? This Adapter's the ONLY Fix!WiFi Nightmare on Windows? Fix Your Connection NOW!
Let’s face it, we’ve all been there. You reach for your Windows laptop, ready to dive into that crucial work presentation, stream your favorite show, or simply scroll through cat videos (no judgment here!). But then… the dreaded spinning circle appears. The Wi-Fi icon in the corner of your screen throws a tantrum, and suddenly, you're adrift in the digital sea, cut off from the world. A Wi-Fi nightmare on Windows is a shared experience, but it doesn't have to be a permanent state of affairs. We are going to delve into the common culprits and arm you with the tools to banish those connection woes for good. Consider this your survival guide to navigating the treacherous terrains of Windows Wi-Fi.
1. The Silent Assassin: Is Your Wi-Fi Really the Culprit?
Before we start frantically clicking and rebooting, let's play detective. Sometimes, the issue isn't your Wi-Fi at all. It could be your internet service provider (ISP) acting up, a hiccup in your router, or even a problem with the website or service you're trying to access.
- Check the Obvious: Start by confirming the basics. Is the Wi-Fi light on your router blinking or solid? A blinking light often signals a problem. Try restarting your router and modem – the classic "turn it off and on again" solution works surprisingly often.
- Test Other Devices: Does your phone, tablet, or another computer connect to your Wi-Fi without issue? If other devices are working fine, the problem is likely localized to your Windows laptop. If all devices are struggling, the issue probably lies with your internet connection or router.
2. Windows’ Wi-Fi Whims: Is It Even Enabled?
This might sound silly, but it's a surprisingly common culprit. Windows, in its infinite wisdom, sometimes decides to… well, disable your Wi-Fi.
- Check the Taskbar: Look for the Wi-Fi icon in your system tray (the area near the clock). If it's grayed out or shows a cross, Wi-Fi is likely disabled.
- Airplane Mode: Make sure Airplane Mode isn't enabled. This will disable all wireless connections, including Wi-Fi. You can find this setting in the Action Center (click the notification icon in the taskbar).
- Network Adapter Settings: Navigate to your Network Connections settings (search for "Network Connections" in the Windows search bar). Make sure your Wi-Fi adapter is enabled. Right-click on the adapter and select "Enable" if it's disabled.
3. Driver Drama: Do You Have the Right Driver?
Drivers are the unsung heroes (or villains) of the tech world. They're essentially the software that allows your hardware, like your Wi-Fi adapter, to communicate with your operating system. Outdated or corrupted drivers can lead to all sorts of connectivity chaos. It’s like trying to speak a language that your computer doesn't understand.
- Update Your Drivers: The easiest way to fix potential driver issues is to update them. Go to Device Manager (search for it in the Windows search bar). Expand "Network adapters," right-click on your Wi-Fi adapter, and select "Update driver." Choose "Search automatically for drivers."
- Roll Back Drivers (If Updates Aren't Working): If you recently updated your drivers and your Wi-Fi started acting up afterward, try rolling back to a previous version. In Device Manager, right-click on your Wi-Fi adapter, select "Properties," go to the "Driver" tab, and click "Roll Back Driver."
- Manufacturer's Website: If Windows can’t find the right driver, visit the website of your laptop manufacturer (e.g., Dell, HP, Lenovo) and download the latest Wi-Fi driver for your specific model.
4. The Hidden Handshake: Troubleshooting Network Configuration
Even with the correct driver, sometimes the problem lies in how Windows is configured to connect to your network. It’s like having a house key, but not knowing which door to open.
- Forget and Reconnect: Sometimes, simply forgetting your Wi-Fi network and reconnecting can work wonders. Go to your Wi-Fi settings, find your network, and click "Forget." Then, reconnect using your password.
- Run the Network Troubleshooter: Windows has a built-in network troubleshooter. Right-click on the Wi-Fi icon in your system tray and select "Troubleshoot problems." It will walk you through some common fixes.
- Network Reset: As a last resort, you can reset your network settings. This will remove all your network configurations and restore them to their default settings. Be aware that you'll likely need to re-enter your Wi-Fi password afterward. Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Advanced network settings > Network reset.
5. Router Rumble: Give Your Router Some TLC
Your router is the bridge between your devices and the internet. It's the conductor of the Wi-Fi orchestra. If it's not performing well, your connection will suffer.
- Restart the Router (Again): Seriously, rebooting your router fixes so many problems. It's like hitting the reset button on life. Unplug it from the power outlet for 30 seconds, then plug it back in.
- Check Router Firmware: Outdated firmware can cause performance issues. Log into your router's settings (usually by typing its IP address into your web browser) and check for firmware updates.
- Router Placement: Where you place your router matters. Keep it away from walls, metal objects, and other electronic devices that can interfere with the Wi-Fi signal. Central locations generally work best.
6. Wi-Fi Signal Strength: Making the Invisible Visible
A weak Wi-Fi signal can lead to slow speeds and dropped connections. It's like trying to hear a faint whisper in a noisy room.
- Check Signal Strength: Look at the Wi-Fi icon in your system tray. The more bars, the stronger the signal.
- Move Closer to the Router: The simplest solution is often the best. Move closer to your router to improve signal strength.
- Wi-Fi Extenders: If you need coverage in a large area, consider using a Wi-Fi extender to boost the signal.
7. Interference Interception: What's Messing with Your Signal?
Wi-Fi signals can be easily disrupted by interference from other devices. It's like trying to have a conversation in a crowded room.
- Microwaves, Bluetooth Devices, and Other Electronics: These devices can interfere with your Wi-Fi signal. Try moving your router and your laptop away from these sources of interference.
- Wireless Radios: Some devices use the same 2.4 GHz frequency as your Wi-Fi router. Test switching your router to the 5 GHz band, which has less interference.
8. Channel Chaos: Selecting the Right Lane
Like choosing the right road for a smooth trip, selecting the right Wi-Fi channel can improve the performance of your connection.
- Wi-Fi Analyzer Apps: These apps let you see which channels your neighbors’ Wi-Fi networks are using. Choose a channel that’s less congested.
- Router Settings: Go to your router's settings and change the Wi-Fi channel. You can usually select a specific channel or set it to "Auto" to let the router choose the best one.
9. Security Snafus: Is Your Firewall the Problem?
Firewalls are designed to protect your computer from threats, but sometimes they can block legitimate connections. It's like having a bouncer who's too strict.
- Check Your Firewall: Go to your Windows Firewall settings (search for "Windows Firewall"). Make sure Wi-Fi is allowed through the firewall.
- Temporarily Disable the Firewall: As a test, you can temporarily disable your firewall to see if it's blocking your Wi-Fi connection. Be sure to re-enable it afterward!
10. Malware Mayhem: The Silent Saboteur
Sometimes, your Wi-Fi problems aren't about your connection at all, but about malicious software running in the background.
- Run a Scan: Run a full scan with your antivirus software to look for malware.
- Malwarebytes: Consider using Malwarebytes, a free and effective anti-malware program that can detect and remove threats that your antivirus might miss.
11. Power Settings Power Play: Optimize Power for Best Performance
Windows power settings can sometimes affect your Wi-Fi performance. If you notice that your connection drops intermittently, consider adjusting these settings.
- Power Plan: Go to Power Options (search for it in the Windows search bar). Make sure your power plan is set to High Performance, or at least Balanced.
- Wireless Adapter Settings: In Device Manager, expand "Network adapters," right-click on your Wi-Fi adapter, and select "Properties." Go to the "Power Management" tab and uncheck "Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power."
12. Windows Updates: The Constant Fixers
While Windows Updates can occasionally cause problems, they often include fixes for Wi-Fi issues.
- Check for Updates: Go to Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update and check for any pending updates. Install them and restart your computer
Fix any Internet and Network Issues with this simple trick
By HowtoInsider Fix any Internet and Network Issues with this simple trick by HowtoInsider
Fix WiFi Not Showing in Settings On Windows 10 Fix Missing WiFi 2025
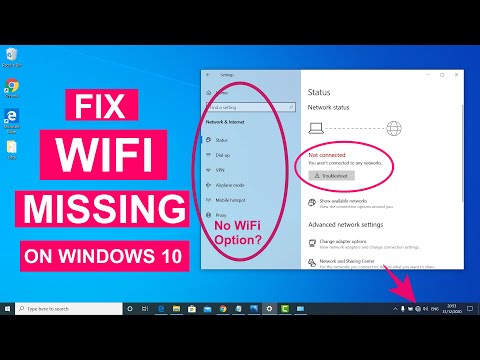
By Sandeep Singh Fix WiFi Not Showing in Settings On Windows 10 Fix Missing WiFi 2025 by Sandeep Singh
If your PC won't connect to the internet shorts pctips tech

By RTC Tutorials If your PC won't connect to the internet shorts pctips tech by RTC Tutorials

Title: How to fix PC not connecting to WiFi
Channel: Scrandalftech
How to fix PC not connecting to WiFi by Scrandalftech
Laptop Working
WiFi Nightmare on Windows? Fix Your Connection NOW!
Is your Windows machine stubbornly refusing to connect to the internet? Are you staring at a frustrating "no internet access" error, or experiencing agonizingly slow speeds? You're not alone. Millions of Windows users grapple with WiFi connectivity issues daily. Fear not, however! We've compiled a comprehensive guide to help you troubleshoot and eradicate those WiFi woes, restoring your connection to its full glory. Let's dive in and banish the WiFi nightmare!
Understanding the Common Culprits Behind WiFi Woes
Before we launch into solutions, it's helpful to understand the usual suspects behind WiFi malfunctions. Problems often stem from a handful of recurring issues, including:
- Driver Conflicts and Corruption: Outdated, corrupted, or improperly installed network adapter drivers are a major source of connection problems. These drivers are the software that allows your computer to "talk" to your WiFi hardware.
- Router Obstructions or Configuration Errors: Your router, the gateway to your internet, might be the source of the problem. Incorrect settings, firmware glitches, or physical obstructions can all interfere with signal transmission.
- Windows Configuration Snafus: Sometimes, Windows itself is to blame. Incorrect network settings, conflicting services, or even temporary glitches within the operating system can disrupt your WiFi.
- Hardware Malfunctions: Although less common, your WiFi adapter itself (the physical component in your computer that receives the WiFi signal) can experience hardware failure.
- Interference: Other devices, especially those operating on the same frequency (2.4GHz), such as microwaves, Bluetooth devices, and even some older cordless phones, can interfere with your WiFi signal.
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting: Your Path to a Stable Connection
We'll meticulously guide you through a series of troubleshooting steps. Follow them sequentially, starting with the simplest checks and progressing toward more advanced solutions. Be patient - sometimes, resolving WiFi problems takes a little detective work.
1. The Basic Checks: Eliminating the Obvious
Before diving into technical solutions, let's eliminate the simplest causes.
- Restart Everything: This may sound overly simplistic, but a simple restart can often resolve transient issues. Restart your computer and your router. Give the router a full minute or two to boot up completely before attempting to reconnect.
- Check the Physical Connections: Ensure the cables connecting your router to your modem (if you have one) are securely plugged in. Also, check the power cables for both devices.
- Verify the Router's Lights: Look at the lights on your router. They should indicate power, internet connection, and WiFi activity. Consult your router's manual for specific light interpretations. If certain lights are off or blinking erratically, it points to a potential problem.
2. Network Adapter Diagnostics: Uncovering Driver Issues
If the basic checks fail, it is time to examine the network adapter. This is the software interface that manages the connection.
- Run the Windows Network Troubleshooter: Windows includes a built-in troubleshooter designed to identify and fix common network problems. Right-click the WiFi icon in your system tray (bottom right corner of your screen) and select "Troubleshoot problems." Windows will then scan for issues and attempt to resolve them automatically.
- Driver Updates: The Key to Compatibility: Outdated or corrupted network adapter drivers are a frequent cause of WiFi issues. Here’s how to update them:
- Open Device Manager: Type "Device Manager" in the Windows search bar and open the application.
- Locate Network Adapters: Expand the "Network adapters" section.
- Identify Your WiFi Adapter: You'll see a list of network adapters, including your WiFi adapter. Look for its name (e.g., "Intel Wireless-AC 9260").
- Update the Driver: Right-click on your WiFi adapter and select "Update driver." Choose "Search automatically for drivers." Windows will search for and install the latest driver.
- Manual Driver Updates: If Windows can't find an updated driver, you might need to download it from the manufacturer's website (Intel, Realtek, etc.). Locate your specific adapter model and download the correct driver for your version of Windows. Then, in Device Manager, right-click the adapter, choose "Update driver," and select "Browse my computer for drivers." Point the system to the folder containing the downloaded driver files.
3. Router Configuration Refinement: Fine-Tuning Your WiFi
Your router's settings can heavily impact WiFi performance and stability.
- Access the Router's Interface: You'll need to access your router's configuration page. Open a web browser and type your router's IP address (typically 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1) into the address bar. You'll need your router's username and password (often found on a sticker on the router itself or in the documentation).
- Check the WiFi Channel: Your router broadcasts WiFi signals on specific channels. Overlapping channels can lead to interference, especially in densely populated areas. Access your router configuration and try switching to a different WiFi channel (1, 6, or 11 are generally recommended for the 2.4 GHz band, as they don't overlap).
- Firmware Updates: Keeping Your Router Current: Router firmware is the operating system for your router. Outdated firmware can cause performance and security issues. Within your router's configuration, look for a "Firmware Update" or "Upgrade Firmware" section. Follow the instructions to update to the latest version.
- Security Settings: Ensure your WiFi network is secured with a strong password using a strong form of encryption, such as WPA2 or WPA3.
4. Windows Network Settings: Taming the Operating System
Sometimes, the problem lies directly within Windows' network configuration.
- Forget and Reconnect to the Network: In Windows, go to Settings > Network & Internet > WiFi, then click "Manage known networks." Select your WiFi network and click "Forget." Then, reconnect to your network by entering your password. This can sometimes refresh your network configuration and resolve connectivity issues.
- Flush the DNS Cache: Your computer stores DNS (Domain Name System) cache data to speed up website loading. If this data is corrupted, it can cause connectivity issues. To flush the DNS cache:
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator: Type "cmd" in the Windows search bar, right-click "Command Prompt," and select "Run as administrator."
- Execute the Command: In the Command Prompt window, type
ipconfig /flushdnsand press Enter.
- Reset the Network Adapter (Advanced): If all else fails, you can try resetting your network adapter. In Settings > Network & Internet > Status, scroll down and click "Network reset." This will reset your network adapter to its default settings. Be aware that you'll need to re-enter your WiFi password afterward.
5. Mitigating Interference: Clearing the Airwaves
WiFi signals are radio waves, susceptible to interference from other devices.
- Identify and Remove Interference Sources: Move your router away from potential sources of interference like microwaves, Bluetooth devices, cordless phones, and other electronics.
- Consider the 5 GHz Band (If Applicable): Most modern routers offer both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz WiFi bands. The 5 GHz band is generally less congested and less prone to interference, but it has a shorter range. If your router and devices support 5 GHz, try connecting to that band.
- Physical Obstructions: Ensure your router is not obstructed by walls, metal objects, or other obstacles that could weaken the signal.
6. Hardware Checks: The Final Frontier
If you've exhausted all other possibilities, it's time to consider hardware issues.
- Test with Another Device: Connect another device (phone, tablet, laptop) to your WiFi. If the other device connects without problems, the issue is likely with your original Windows machine's hardware or software.
- WiFi Adapter Failure: In rare cases, your WiFi adapter may have failed. If you’re comfortable doing so, you could try reseating the adapter or replacing it. Consult a computer repair professional if you're not comfortable performing these tasks.
- Router Hardware Failure: There is a minute possibility that your router's hardware may be failing. Try resetting it to factory settings using the reset button (usually a small button on the back or side) or replace your router.
Maintaining a Healthy Connection: Proactive Measures
Once you've fixed your WiFi problems, it's essential to take steps to prevent future issues.
- Regular Driver Updates: Make it a habit to check for driver updates for your network adapter regularly.
- Router Maintenance: Regularly check your router's firmware and update it when new versions are available.
- Security Practices: Keep your WiFi password strong and change it periodically.
- Hardware Monitoring: Keep an eye out for any signs of hardware problems, such as strange noises or overheating.
- Avoid Obstructing Your Router: Ensure that your router has good ventilation.
By systematically following these steps, you'll be well-equipped to conquer your Windows WiFi woes and enjoy a stable, reliable internet connection. Remember to be patient, methodical, and persistent. The solution to your WiFi
