cannot connect laptop to wifi windows 7
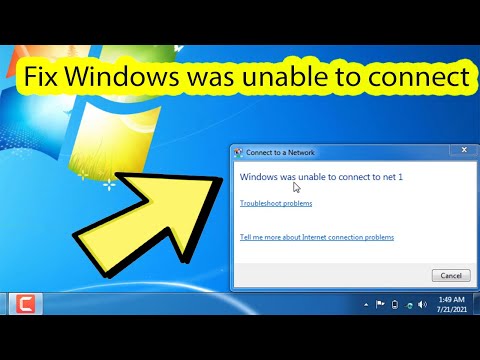
Title: Windows was unable to connect wifi windows 7 Laptop and Desktop
Channel: IT Magics
Windows was unable to connect wifi windows 7 Laptop and Desktop by IT Magics
laptop cannot connect to wifi windows 7, laptop can t connect to wifi windows 7, my laptop cannot connect to wifi windows 7, hp laptop cannot connect to wifi windows 7, laptop won t connect to wifi windows 7, cannot connect to internet on laptop windows 7, why is my windows 7 laptop not connecting to wifi
Windows 7 WiFi Nightmare? FIX Your Laptop Connection NOW!
Windows 7 WiFi Woes? Conquer Those Connection Demons!
Let's face it. We depend on the internet. It fuels our work, connects us to loved ones, and entertains us. But what happens when the WiFi on your trusty Windows 7 laptop throws a wrench in the works? Suddenly, your digital life screeches to a halt. That dreaded “limited connectivity” message isn't just annoying; it's a productivity killer. Fortunately, you don't need to resign yourself to a wired existence. Instead, take action and reclaim control! This guide arms you with the knowledge to vanquish those WiFi connection problems.
The Phantom of the Network: Identifying the Culprit
First, let's diagnose the situation. Is your WiFi completely AWOL, or just spotty? Can other devices connect, or is it just your Windows 7 machine that’s suffering? Pinpointing the issue directs us to the right solution. Moreover, consider external factors. A router reboot is often the simplest fix. However, it may not be that straightforward. So, let’s delve deeper. We shall get to the root of the problem.
Your laptop might be the issue. Or perhaps it is your router. Possibly, it is something else entirely. Therefore, consider these elements. Check the physical connection. Ensure your WiFi switch (if your laptop has one) is flipped on. It's a basic step, yet easily overlooked. Afterward, examine your network adapter settings. They may need a simple tweak.
Unleashing the Network Adapter: A Tech Tune-Up
Your network adapter is the unsung hero. It is the interface between your laptop and the digital world. It manages the WiFi signals. Therefore, start by accessing the Device Manager. You can find it in the Control Panel. Or even search for it in the Start menu. Locate "Network adapters" and expand the list.
Right-click on your wireless network adapter. Select "Properties." The "Driver" tab holds the key. Ensure your driver is up-to-date. If not, click "Update Driver." Windows will search for updates. If not, you can manually download the latest driver from your manufacturer's website. This is also a worthwhile idea.
Next, navigate to the "Power Management" tab. Uncheck "Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power." This prevents the adapter from going to sleep and disconnecting. Then, apply these changes. Restart the adapter if needed.
Deciphering the Wireless Network Settings: A Configuration Check
Incorrect network settings can create chaos. So, let's ensure your WiFi connection is correctly configured. Access the Network and Sharing Center. You can access it via the Control Panel. Select "Manage wireless networks" from the left pane. Here, you'll see a list of saved networks.
Right-click on your affected WiFi network. Select "Properties." The "Security" tab is crucial. Verify the security type (e.g., WPA2-Personal) and the encryption type (e.g., AES). Also, verify the network security key is correct. This is usually your WiFi password. Incorrect security settings can block the connection.
If everything appears correct, try forgetting the network. Then, reconnect. Enter the network password. This often clears minor configuration glitches.
Channel Surfing: Optimizing Your Router's Performance
Consider your router. Routers broadcast signals on different channels. Nearby routers operating on the same channel can cause interference. So, it is vital to optimize your router's performance. Access your router's configuration page. This usually involves typing your router's IP address (often 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1) into your web browser. Log in using your router's credentials.
Look for the wireless settings. You’ll find the current channel your router is using. Experiment with different channels. Avoid channels already used by other devices. Also, consider using a WiFi analyzer app on your phone. This can assist in identifying the least congested channel.
Troubleshooting the Troubleshooters: Windows' Helpful Hand
Windows 7 has built-in troubleshooting tools. Use them. They can pinpoint and fix common problems. Right-click the WiFi icon in the system tray. Select "Troubleshoot problems." Windows will scan for issues and suggest solutions.
Follow the on-screen prompts. Let Windows attempt to fix the connection. It may resolve the issue. However, don’t rely on it as a guaranteed cure. Sometimes, it may only offer a suggestion. Ultimately, troubleshooting is a process.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Solutions
If all else fails, it's time to escalate the troubleshooting. Consider the following:
Firewall Interference: Temporarily disable your firewall. See if it is blocking the connection. If it is, adjust the firewall settings to allow your network connection. Afterwards, add the necessary exceptions.
Network Adapter Reset: Resetting the network adapter to its default configuration may resolve issues. Go to the Network and Sharing Center. Change adapter settings. Right-click on your wireless adapter. Then, select "Disable." Wait a few seconds, and then select "Enable" again.
System Restore: Rolling back your system to a previous configuration might also provide a solution. This will reverse recent changes. This method is only effective if you recently made system modifications.
External WiFi Adapter: If your internal adapter is faulty, obtaining an external USB WiFi adapter is another option. It provides a quick fix. This bypasses the internal adapter.
The Victory Dance: Celebrating a Successful Connection
There you have it! You went through multiple troubleshooting steps. With patience and persistence, you can banish those WiFi woes. After successfully reconnecting, the internet feels like a triumph. Finally, enjoy your newly restored connection! And, hopefully, your Windows 7 laptop connects with ease. Now that your WiFi is working, you're all set. Therefore, go online and enjoy!
HP Laptop WiFi Nightmare? FIX It NOW!Windows 7 WiFi Nightmare? FIX Your Laptop Connection NOW!
How many times have you screamed at your laptop? I know I have! That frustrating spinning wheel of death, the endless "connecting…" message, or the utter silence when you desperately need to check your email. If you're still rocking a Windows 7 machine (hey, no judgment here, I love a classic!), you've probably encountered the dreaded WiFi woes. Forget about pulling your hair out – we're here to troubleshoot, diagnose, and get you back online in a flash. Think of this blog post as your personal WiFi whisperer guiding you through the technical maze.
1. The WiFi Apocalypse: Why Windows 7 Can Be a Connection Craziness
Let's be honest, Windows 7 isn't exactly a spring chicken in the tech world. It's like that reliable, but slightly grumpy, old friend who sometimes just… doesn't want to cooperate. Age, updates, and the ever-evolving world of WiFi standards can create a perfect storm of connectivity issues. Don't panic! Like a detective examining clues, we'll pinpoint the culprits behind your WiFi woes. Was it the rogue update? Is the driver outdated? Or is it just the gremlins playing tricks in your router?
2. First Stop: The Obvious Suspects – Troubleshooting 101
Before you dive into complex fixes, let's start with the basics. It's like checking if your car has gas before you start diagnosing engine problems.
- Restart Everything: Seriously, the simplest solution is often the best. Restart your laptop and your router. It’s like hitting the reset button for your internet connection.
- Check the Physical: Is the WiFi switch (often a physical button on the side or front of your laptop) turned on? Make sure it’s not accidentally disabled.
- Internet Connection: Ensure the router itself is connected to the internet. Check the lights on the router – are they flashing, solid, or indicating an error?
- Distance Matters: Are you too far from your router? Thick walls or other electronic devices can interfere with the signal. Consider moving closer.
3. Diving Deeper: Diagnosing Your WiFi Dilemma
If the basics didn't work, it's time to get a little more hands-on. Think of it like performing a patient examination to determine what's going on.
- Network Name: Open the Network and Sharing Center (search it in the Start menu). See if your WiFi network even shows up. If it doesn't, the problem is likely with your laptop's WiFi adapter or your router's broadcasting settings.
- "Limited Access" Warning: A "Limited Access" message suggests your laptop is connecting to the router but not getting a valid IP address from it. This is a common issue, and we'll tackle it later.
- "Cannot Connect to This Network" Error: This message usually means your laptop is rejecting the router's signal. Could be a password problem or a configuration issue in your router.
4. Driver Dysfunction: The Root of Many WiFi Problems
Drivers are the software that allows your computer to "talk" to hardware, including your WiFi adapter. Outdated or corrupted drivers are often the reason for lost connections. Think of them like the translators between your laptop and your WiFi.
- Updating Your Driver: The easiest way is through Device Manager (again, search in the Start menu). Find "Network Adapters," right-click on your WiFi adapter, and select "Update driver." Let Windows search automatically.
- Manual Driver Updates: If the automatic update fails, you might need to download the latest driver from your laptop manufacturer's website. You'll need your laptop's model number.
- Roll Back: You can roll back to a previous driver if a recent update caused the problem. In Device Manager, right-click your WiFi adapter, go to "Properties," and choose "Driver." If the "Roll Back Driver" option is available, try it.
5. IP Address Troubles: Fixing the "Limited Access" Issue
As I mentioned earlier, "Limited Access" is a frequent culprit. It's as though your laptop can see the router, but the router can't quite see your laptop's IP address. It's like a lost package.
- Automatic Configuration: Make sure your WiFi adapter is set to obtain an IP address automatically. In the Network and Sharing Center, click "Change adapter settings," right-click your WiFi connection, go to "Properties," and select "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)". Ensure "Obtain an IP address automatically" is selected.
- Release and Renew: Open the Command Prompt (search in the Start menu and type "cmd"). Type the following commands, pressing Enter after each:
ipconfig /releaseipconfig /renew
- Static IP (Advanced): If the above fails, you can try assigning a static IP address and DNS servers. This requires a bit more technical knowledge, so look up specific instructions for your router's settings online from a reliable source.
6. The Router's Revenge: Checking Your Router Settings
Sometimes, the problem isn't your laptop, but your router's settings. It is a lot like finding an issue with the power grid.
- Check Your Router's Admin Panel: You'll need your router's IP address (usually 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1; you can find your router's IP address in the Network and Sharing Center) and the administrator username and password (often found on the router's sticker or in its documentation).
- Security Settings: Ensure your WiFi security is set to WPA2-PSK (AES) or WPA3. Avoid WEP, which is outdated and insecure.
- Channel Congestion: Your router broadcasts on a specific channel. Neighbors' routers on the same channel can cause interference. You can try changing the WiFi channel in your router's settings. Most routers offer automatic channel selection.
- Firmware Updates: Ensure your router’s firmware is up to date. Older firmware can have security vulnerabilities and performance issues.
7. Power Management Woes: Letting Your Adapter Thrive
Windows sometimes puts your WiFi adapter to sleep to save power. This can sever your connection or make it slow.
- Check Power Settings: Go to Device Manager, find your WiFi adapter, right-click, select "Properties," go to the "Power Management" tab, and uncheck "Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power."
8. Antivirus Antics: Potential Conflict
Sometimes your security software gets a little too overzealous and blocks your WiFi connection.
- Temporarily Disable Antivirus: As a test, try temporarily disabling your antivirus software to see if it's interfering. If this fixes the issue, you may need to adjust your antivirus settings to allow your WiFi connection.
9. The Firewall Factor: Is It Blocking You?
Similar to your security software, Windows Firewall can block the connection to your WiFi adapter.
- Check Firewall Settings: Open Windows Firewall (search in the Start menu). Make sure your WiFi adapter is allowed in your firewall settings.
- Reset Firewall: If you're unsure, resetting your firewall to its default settings might resolve the issue, but this will remove any custom rules you've created.
10. Resetting Network Settings: A Last Resort
If almost everything else fails, you could try to reset your network settings.
- Run Network Troubleshooter: The built-in Windows Network Troubleshooter can often diagnose and fix common network problems. It can be found in the Network and Sharing Center.
- Network Reset: In Windows settings (search in the Start menu), go to "Network & Internet," then "Status," and then "Network reset." This will reset your network adapters, and you may need to re-enter your WiFi password.
11. The Wireless Adapter Itself: Hardware Hurdles
Sometimes the hardware inside your laptop is starting to fail. It's life, unfortunately.
- External USB Adapter: If all else fails, consider using an external USB WiFi adapter. It's a simple, cost-effective solution.
12. Interference Investigation: Shielding Your Signal
The world is awash with signals, and those signals can cause problems.
- Microwave Menace: Keep your laptop away from microwave ovens when using WiFi.
- Other Electronics: Avoid placing your laptop near other electronics that emit electromagnetic interference (EMI).
- Obstruction Obstacles: Avoid physical obstruction such as thick walls, doors, metal objects, etc.
13. The SSID Shuffle: Rethinking Your Network Name
Sometimes, a hidden or special character in your SSID name causes problems.
- Try Using a Simple SSID: Consider creating a new, simple SSID name (without special characters) for your network, and see if your laptop connects.
14. Router Restart Rituals: Keeping it Happy
Sometimes, all your tech requires is a little bit of maintenance.
- Regular Reboots: Rebooting your router regularly can help prevent connection issues.
15. The Ultimate Solution: Upgrade Time?
Let's be candid, if you’ve tried everything in this guide, and the problem persists, it might
Dell Inspiron i5: SHOCKING 2GHz WiFi Limit! (Upgrade Guide Inside)Not connected no connections are available windows 7 laptop

By IT Magics Not connected no connections are available windows 7 laptop by IT Magics
Cara mengatasi Wifi adapter hilang windows 7,8,10
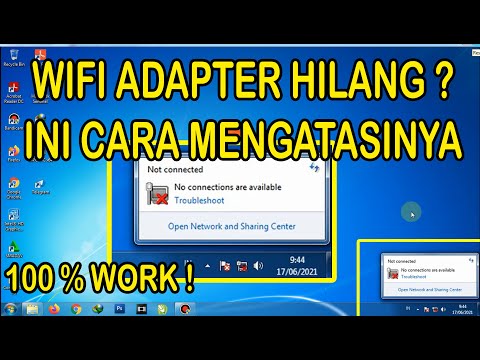
By Ani Saja Cara mengatasi Wifi adapter hilang windows 7,8,10 by Ani Saja
Wireless Network Connection Enabled but Not connected Fix Windows 7
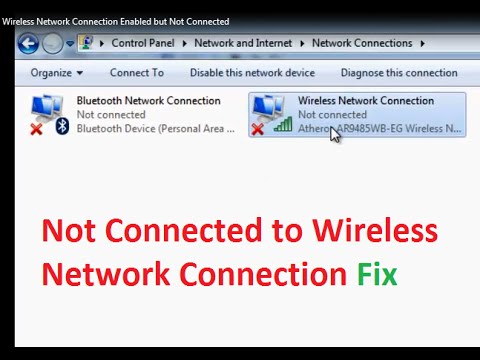
By troubleshooterrors Wireless Network Connection Enabled but Not connected Fix Windows 7 by troubleshooterrors
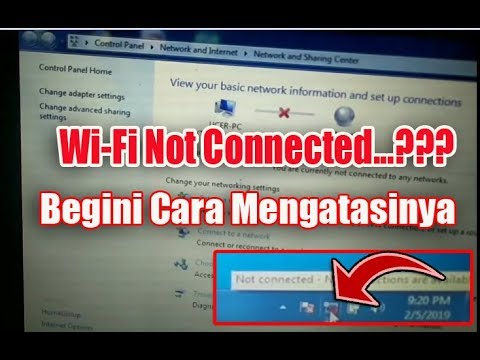
Title: You Are Not Connected to Any Network Fix WiFi
Channel: asal ngelik
You Are Not Connected to Any Network Fix WiFi by asal ngelik
Laptop Wifi Connect
Windows 7 WiFi Nightmare? FIX Your Laptop Connection NOW!
Is your Windows 7 laptop stubbornly refusing to connect to the internet? Are you staring in frustration at a lack of WiFi signal or a painfully slow connection? You're not alone. Many users have wrestled with WiFi woes on this now-classic operating system. But take heart! We've compiled a comprehensive guide, packed with specific solutions, to banish your connectivity demons and get you back online. Let's dive in and transform that WiFi nightmare into a smooth, reliable experience.
Diagnosing the WiFi Dilemma: Identifying the Source of the Problem
Before you frantically start clicking buttons, we need to understand what exactly is causing your connection issues. Is the problem sporadic or consistent? Does it affect all networks, or just a specific one? Understanding the nature of the problem will help pinpoint the most effective solution.
- No WiFi Networks Detected: If your laptop isn’t even seeing available WiFi networks, the issue is likely with your network adapter, its drivers, or possibly the physical WiFi switch on your laptop (if it has one).
- Limited Connectivity or No Internet Access: Your laptop sees the network but can't connect, or it connects but has no internet access. This suggests a problem with network authentication, router settings, or your internet service provider (ISP).
- Slow Connection Speeds: Even when connected, is your browsing painfully slow? This could be due to several factors, including signal strength, channel interference, or limitations on your internet plan.
- Intermittent Disconnections: Dropping the WiFi connection frequently is incredibly frustrating and points to a problem with the network adapter's stability, signal strength, or router compatibility.
Now, let's get to the solutions.
Driver Dilemmas: Ensuring Your Network Adapter is Up-to-Date and Functional
Outdated or corrupted network adapter drivers are notorious culprits behind WiFi problems. Think of the driver as the translator between your laptop's hardware and the operating system. When the translation breaks down, so does your connection.
- Accessing Device Manager: The Device Manager is your central hub for managing hardware. To access it, click the Start button, type "devmgmt.msc" in the search bar, and press Enter.
- Locating Your Network Adapter: In Device Manager, expand the "Network adapters" section. Your WiFi adapter will be listed here (it might be labeled something like "Wireless Network Adapter" or specific to its manufacturer, like "Intel Wireless").
- Updating Your Driver: Right-click on your WiFi adapter and select "Update driver." Choose "Search automatically for updated driver software." Windows will attempt to find the latest driver online. If it succeeds, follow the prompts to install it.
- Manual Driver Update: If the automatic update fails, you can manually download the latest driver from the manufacturer's website (e.g., Intel, Broadcom, Realtek) for your specific adapter model. You'll need to know the model number, which you can usually find listed in Device Manager or on the adapter itself. Download the driver and then, in Device Manager, right-click the adapter, select "Update driver," and choose "Browse my computer for driver software." Point it to the downloaded driver file.
- Driver Rollback: If a recent driver update caused the problem, you can roll back to a previous version. Right-click the adapter in Device Manager, select "Properties," go to the "Driver" tab, and click "Roll Back Driver" if the option is available.
- Uninstalling and Reinstalling Drivers: Sometimes, a driver is so corrupted that a complete removal and reinstall is required. Right-click the adapter in Device Manager and choose "Uninstall." Restart your computer, and Windows should automatically reinstall the appropriate driver.
The Physical WiFi Switch: Is It On?
Many laptops, especially older ones, include a physical switch (often on the side or front) that toggles the WiFi on and off. It might be as simple as a small sliding switch or a combination key (like Fn + a function key). Double-check that this switch is in the "on" position.
Network Settings Navigation: Troubleshooting Your Connection Configuration
Incorrect network settings can wreak havoc on your WiFi connection. We will explore some of the most common culprits.
- Checking IP Address Configuration: Right-click on the network icon in your system tray (the bottom right corner of your screen) and select "Open Network and Sharing Center." Click on "Change adapter settings" on the left side. Right-click on your wireless network adapter, select "Properties," and then double-click "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)." Make sure "Obtain an IP address automatically" and "Obtain DNS server address automatically" are selected. If not, select these options and click "OK."
- Network Reset: Consider a network reset. In "Network and Sharing Center," click on "Change adapter settings" on the left side. Right-click on your wireless network adapter, select "Disable" and then "Enable" to reset the network adapter.
- Forget and Reconnect to the Network: Have you tried forgetting the network and reconnecting? Right-click on the network icon in your system tray and select "Open Network and Sharing Center" then click "Manage wireless networks" on the left side. Select your WiFi network and click "Remove." Then, reconnect to the network by selecting it from the list of available networks and entering the password.
- Firewall Interference: Your firewall might be blocking the connection. Check your Windows Firewall settings to ensure that your WiFi adapter is allowed to communicate with the internet and that the network is classified correctly (e.g., as a private network, not a public one). You can usually find these settings by searching for "Windows Firewall" in the Start menu.
- Proxy Settings Check: If you are using a proxy server, ensure that the settings are correct. In Internet Explorer (even if you don't use it regularly), go to "Tools" > "Internet Options" > "Connections" tab > "LAN settings." Disable "Use a proxy server for your LAN" if you're not intentionally using one.
Router Realities: Examining Your Router's Role in the Equation
Your router is the gateway to the internet, and problems with it can directly impact your laptop's WiFi.
- Router Reboot: The simplest and often most effective solution is a good old-fashioned reboot of your router. Unplug the router from its power source for 30 seconds, then plug it back in. Wait for it to fully boot up (usually a couple of minutes) and then try connecting your laptop again.
- Router Firmware Updates: Outdated router firmware can cause compatibility issues. Log in to your router's configuration page (usually by typing its IP address, such as 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1, into your web browser) and look for a firmware update option. Follow the manufacturer's instructions to update the firmware safely.
- Channel Congestion: WiFi routers broadcast on different channels. If your neighbors' routers are using the same channel as yours, it can lead to interference and slow speeds. Access your router's configuration page and try changing the WiFi channel. Experiment with different channels (1, 6, and 11 are often recommended).
- Signal Strength and Placement: Ensure your router is placed in a central location, away from obstructions (walls, metal objects) that can block the WiFi signal.
- Router's Security Settings: Make sure your router's security settings are up-to-date. WPA2 or WPA3 encryption is recommended for security.
- Router Maximum Users: Check your router settings to make sure there are not too many users connected to the network.
- Reset Router to Default: If none of the above settings have resolved the issue, try a router reset to its default settings.
Signal Strength and Environmental Factors: Optimizing Your Wireless Environment
Even with a properly configured network, physical factors can hinder your connection.
- Distance and Obstacles: The further you are from your router, the weaker the signal. Thick walls, metal objects, and other electronic devices can also interfere with the signal. Try moving closer to the router or relocating the router to a more open area.
- Interference from Other Devices: Microwave ovens, Bluetooth devices, and other wireless devices can cause interference. Try turning off these devices temporarily to see if it improves your WiFi performance.
- Antenna Position: Some laptops have antennas that can be adjusted. Try changing the angle of your laptop's antenna to see if it improves the signal.
- External WiFi Adapters: If your laptop's internal WiFi adapter is consistently problematic, consider using an external USB WiFi adapter. This can sometimes provide a more stable and powerful connection.
Power Management Pitfalls: Preventing WiFi Shutdowns
Windows 7's power-saving features can sometimes inadvertently disable your WiFi adapter.
- Power Plan Settings: Access "Power Options" from the Control Panel. Click "Change plan settings" next to your current power plan and then click "Change advanced power settings."
- Wireless Adapter Settings: In the advanced settings, expand "Wireless Adapter Settings" and then "Power Saving Mode." Make sure it is set to "Maximum Performance" or "Off." This prevents Windows from turning off the adapter to save power.
- Adapter Allow Off: Further down
