how to enable wifi in laptop windows 7

Title: How To Enable WiFi Internet Connection In Windows 7
Channel: MDTechVideos International
How To Enable WiFi Internet Connection In Windows 7 by MDTechVideos International
how to enable wifi in laptop windows 7, how to connect wifi in laptop windows 7, how to connect wifi in laptop windows 7 ultimate, how to activate wifi in laptop windows 7, how to enable wifi in dell laptop windows 7, how to connect internet in laptop windows 7, how to connect wifi in dell laptop windows 7, how to connect wifi in acer laptop windows 7, how to connect wifi in hp laptop windows 7, how to connect wifi in toshiba laptop windows 7
Windows 7 WiFi Nightmare? Solved in 60 Seconds!
Windows 7 WiFi Woes? Stop the Frustration!
Ever stared bleary-eyed at a blinking WiFi icon on your faithful Windows 7 machine? It’s a familiar tale, isn’t it? Suddenly, the internet connection vanishes. Panic sets in, especially when deadlines loom. But what if I told you resolving these WiFi headaches doesn't require a degree in computer science? In fact, solutions are often within reach. Let’s banish those connection nightmares.
The Phantom WiFi: Unmasking the Culprit
First things first: let's identify the potential villains. The issue may stem from various sources. Perhaps a driver update went awry. Maybe there's a conflict with your network adapter. Sometimes, simple settings are the root cause. Don't despair. We’ll examine common culprits. So, be ready to troubleshoot.
Step 1: The Restart Ritual (And Why It Matters)
Before diving into complex solutions, let's start with the simplest. Restart your computer. It's basic, I know. It’s often the most effective. As a result, it clears temporary glitches. Furthermore, this allows Windows to refresh its connection to the network. However, don’t just shut it down. Perform a full reboot. Shutting down and turning it back on can help resolve many issues.
Step 2: Driver Detective Work - Ensuring Compatibility
Next, consider your network adapter drivers. These are the software instructions connecting your computer to WiFi. Outdated or corrupted drivers can cause chaos. Fortunately, updating drivers is usually simple. Therefore, first, right-click 'My Computer' or 'This PC.' Choose 'Manage.' Expand ‘Device Manager.’ Locate 'Network Adapters.' Right-click on your adapter. Then, select 'Update Driver Software.' Windows will search for updated drivers automatically. Alternatively, visit your adapter manufacturer’s website. Download and install the latest drivers directly.
Step 3: Wireless Profile Pruning - Clean Up the Clutter
Windows 7 stores WiFi network profiles. Over time, these can accumulate. Moreover, they can lead to confusion. Sometimes, these profiles become corrupted. Therefore, it is best to prune them. Here’s how: Open the 'Network and Sharing Center' via Control Panel. Select 'Manage wireless networks'. Delete any obsolete networks. Keep only the ones you actively use. Restart your computer after this step.
Step 4: The Troubleshooter's Toolkit - Letting Windows Help
Windows 7 has built-in troubleshooting tools. These tools are surprisingly effective. They will automatically diagnose many WiFi problems. Access the troubleshooter. Right-click the WiFi icon in your system tray. Choose 'Troubleshoot problems.' Windows will guide you through the process. Let it scan for issues. Follow its recommendations carefully.
Step 5: IP Address Renewal - A Fresh Start for Your Connection
Sometimes, your computer gets stuck with an outdated IP address. This prevents it from connecting. Renewing it can bring things back to life. Open the Command Prompt. Type 'ipconfig /release' and press Enter. Then, type 'ipconfig /renew' and press Enter. This action forces your computer to request a new IP address. As a result, your connection may be restored.
Step 6: Check the Physical Hardware - The Antennas Matter
Ensure your WiFi router is functioning correctly. Check the lights on the router. Verify that the internet connection coming into the router is stable. Also, check the physical connection. Make sure all cables are securely connected. Try restarting your router. This often refreshes its settings. If the router is the issue, you may need to contact your internet service provider.
Step 7: Advanced Settings Tweaks - Delving Deeper (If Needed)
If the previous steps fail, explore advanced settings. Access your network adapter properties in 'Device Manager'. Experiment with different settings. Consider disabling power-saving mode and checking your security settings. Check your firewall settings to ensure they don't block your WiFi. However, these configurations are more technical.
Seize Control of Your Connection
These steps will hopefully restore your Windows 7 WiFi. Remember, troubleshooting is a process. It may take a few tries. Most importantly, stay positive. Don’t feel intimidated by technology. If you still face issues, seek online resources. Websites and forums provide user-generated answers. Soon, you’ll regain your internet access.
Is Your Laptop's Wi-Fi Killing Your Productivity? This FIX Will SHOCK You!Windows 7 WiFi Nightmare? Solved in 60 Seconds!
Hey everyone! Remember the good old days of Windows 7? While it holds a special place in my heart (it's where I first learned to build my own gaming PC!), let's be honest, it could be a frustrating beast, especially when your WiFi decided to take a vacation. I've lost count of the times I've been staring at a blinking "No Internet Access" icon, tearing my hair out just because I couldn't connect to the web! And let's be honest, we've all been there, right? Well, consider this your SOS signal answered because we're diving headfirst into slaying the Windows 7 WiFi dragon, and we're going to do it FAST.
1. The WiFi Woes: Why Windows 7 Can Sometimes Be a Pain
First things first, let's acknowledge the problem. Windows 7, bless its heart, isn't exactly the most intuitive when it comes to WiFi troubleshooting. Think of it like trying to understand a grumpy old sailor – you need to know the right lingo to get anything done! Common culprits? Outdated drivers, conflicting IP addresses, and security settings gone rogue. These are the gremlins that love to mess with your connection, leaving you feeling more isolated than a castaway on a desert island. Ever felt like your WiFi was playing hide-and-seek? Yeah, we get it.
2. Are You Actually Connected? The Obvious Check (But Don't Skip It!)
Sounds silly, right? But before we dive into complex fixes, let's cover the basics. Are you actually connected to your WiFi network? Double-check the system tray (that little area in the bottom right corner of your screen). See the WiFi icon? Does it have a good connection signal (like a few bars)? If it's showing a red "X" or a yellow warning triangle, we've got a problem. Think of it like checking if your car is plugged into the wall before complaining about the battery dying. Sometimes, the simplest things are the most overlooked.
3. The Driver Dilemma: Updating Your Network Adapter ASAP
Drivers are the magical translators that allow your computer to "speak" to your WiFi adapter. Outdated drivers are like trying to order pizza in a language nobody understands. Your computer just can't "hear" the signals from your router! Here's how to update them:
- Step 1: Open Device Manager: Click the Start button, type "Device Manager" in the search bar, and press Enter.
- Step 2: Expand Network Adapters: Click the little arrow next to "Network adapters" to expand the list.
- Step 3: Find Your WiFi Adapter: Look for your WiFi adapter (it might be labeled as "Wireless Network Adapter" or something similar).
- Step 4: Right-Click and Update: Right-click on your WiFi adapter and select "Update driver."
- Step 5: Choose the Update Method: Select "Search automatically for updated driver software." Windows will attempt to find and install the latest drivers.
- Step 6: Restart, Restart, Restart! After the update, restart your computer. Think of a restart as hitting the "reset" button – it often clears up all sorts of gremlins.
4. The IP Address Tango: Getting Your Network's Groove Back
Sometimes, your computer gets confused about its IP address. An IP address is like your home address on the internet, and if it's incorrect, you won't be able to find your way online. This might sound techy, but don't worry, it's easy to fix!
Option 1: Automatic Address: Go back to those network settings (right-click the WiFi icon in the system tray and select "Open Network and Sharing Center"). Click on "Change adapter settings." Right-click on your WiFi connection and select "Properties." Find "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)" and double-click it. Ensure that "Obtain an IP address automatically" and "Obtain DNS server address automatically" are selected. Click OK, and then close all windows.
Option 2: Release and Renew (If the above doesn't work): Open the Command Prompt as an administrator (search for "cmd," right-click, and select "Run as administrator"). Type
ipconfig /releaseand press Enter. Then, typeipconfig /renewand press Enter. Restart your computer. This forces your computer to get a fresh IP address from your router.
5. Flushing the DNS: Clearing Out the Web's Cobwebs
DNS (Domain Name System) is the internet's phonebook. If this phonebook gets corrupted, then you might struggle to access websites correctly. Imagine your internet browser is a car, and the DNS servers are all the road maps. The issue could be with the maps. Flushing your DNS is like clearing out the old, confusing maps, and getting some new, updated ones.
- Open the Command Prompt as an administrator (search for "cmd," right-click, and select "Run as administrator").
- Type
ipconfig /flushdnsand press Enter. - Type
ipconfig /registerdnsand press Enter. - Restart your computer.
6. Firewall Frenzy: Ensuring the Gatekeeper Isn't Blocking You
Your Windows Firewall (the gatekeeper of your computer) sometimes goes a little overboard and blocks your WiFi connection. This can often happen after a Windows update. Time to check!
- Open Windows Firewall (search for "Firewall" in the Start Menu).
- Click on "Allow an app or feature through Windows Firewall."
- Make sure your WiFi adapter is allowed through the firewall. You might need to click "Change settings" and check the boxes next to your WiFi adapter under both "Private" and "Public" networks.
- Click OK.
7. Troubleshooting the Router: The Ultimate Power Move
Sometimes, the problem isn't your computer; it's the router! Think of your router as the central hub of your WiFi network. If the hub is offline, nobody gets online. Here's how to give your router a quick check-up:
- The Reboot Ritual: Unplug your router and modem (if you have a separate modem) from the power outlet. Wait about 30 seconds. Plug them back in. This is often the magic bullet to fixing most router issues.
- Check the Lights: Look at the lights on your router. Are any of them red or blinking? That could indicate a problem.
- Check Router Settings: Access your router's settings (usually by typing its IP address – often something like 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1 – into your web browser). Make sure your WiFi network is enabled and broadcasting.
8. Wireless Network Diagnostics: Windows’ Hidden Hero
Windows 7 has a built in network troubleshooter that is often overlooked. It can often pinpoint the problem and offer a solution.
- Right-click the WiFi icon in your system tray.
- Select "Troubleshoot problems."
- Follow the on-screen instructions.
- The system will analyse the issue and provide suggestions.
9. Security Settings Showdown: WPA2 vs. WPA3 and Beyond
Your security settings can be a potential source of issues. Windows 7 is a bit old. Here are some considerations:
- Check Supported Protocols: Your router should support WPA2 and maybe WPA3. Check the settings on your router.
- Compatibility Concerns: Ensure your Windows 7 system is compatible with the security protocols.
10. Signal Strength SOS: Moving Closer to the Source
Is your signal weak? The physical distance between your WiFi router and your computer can significantly impact your connection strength. Think of the WiFi signal like a radio broadcast – the further away you are, the weaker the signal.
- Move Closer: If possible, move your computer closer to the router.
- Obstacle Course: Walls and other obstacles can disrupt the signal. Try to minimize obstructions between your computer and the router.
- Router Placement: Make sure the router is in a central and open location.
11. The "Airplane Mode" Antidote: A Quick Reset
Sometimes, a simple reset is all that's needed. Like restarting the computer, restarting your network connection can often solve the problem.
- Click the WiFi icon in the system tray.
- Turn off WiFi. Wait a few seconds.
- Turn WiFi back on.
12. Compatibility Mode: A Blast From the Past (Maybe!)
For some older network adapters, running the network adapter in compatibility mode can work wonders.
- Open Device Manager (as explained in section 3).
- Right-click your WiFi adapter.
- Select "Properties."
- Go to the "Driver" tab.
- Click on "Update Driver."
- Select "Browse my computer for driver software."
- Click on "Let me pick from a list of device drivers on my computer."
- Select an older driver version (if available) or a generic, older driver.
- Click "
How to turn on wifi in windows 7

By Being Selftech How to turn on wifi in windows 7 by Being Selftech
Not connected no connections are available windows 7 laptop

By IT Magics Not connected no connections are available windows 7 laptop by IT Magics
How to enable your network connection in Windows 7
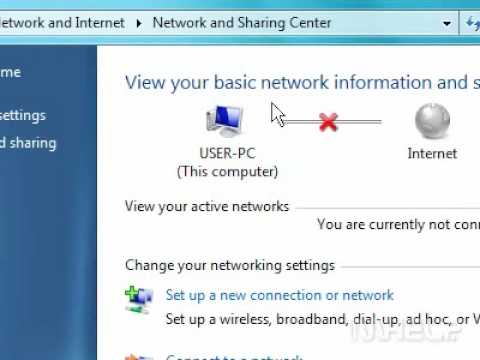
By MHELP2U How to enable your network connection in Windows 7 by MHELP2U

Title: CARA MENGAKTIFKAN WIFI DI WINDOWS 7
Channel: Rdn Channel
CARA MENGAKTIFKAN WIFI DI WINDOWS 7 by Rdn Channel
Wifi On Laptop Phone
Windows 7 WiFi Nightmare? Solved in 60 Seconds!
Let's face it; dealing with WiFi woes can feel like navigating a digital minefield. You're eager to browse, stream, or work, only to be met with the dreaded "limited connectivity" message or agonizingly slow loading times. For those clinging to the dependable, yet aging, Windows 7 operating system, these WiFi problems can seem particularly persistent, prompting users to tear their hair out in frustration. Fear not! We've compiled a streamlined, easy-to-follow guide that will have your Windows 7 machine connected and cruising on the internet in under a minute. Forget the complicated tech jargon and endless troubleshooting forums. We're diving straight into the practical solutions you need, right now.
Understanding the Common Culprits Behind WiFi Problems
Before we leap into solutions, it's helpful to understand the usual suspects behind WiFi connectivity issues in Windows 7. While the problems may vary, several issues repeatedly plague users. These issues include problematic network adapter drivers, incorrect network settings, router incompatibility, and interference from other electronic devices. Identifying the source of the problem can drastically speed up the resolution process. We'll systematically address each of these areas, ensuring you have a comprehensive toolkit to tackle whatever WiFi gremlins are haunting your system.
Step 1: Restart Your Windows 7 Computer and Router – The First Line of Defense
It may sound overly simple, but the classic "turn it off and on again" approach remains remarkably effective. Before you dive into more complex solutions, give your Windows 7 PC and your router a fresh start. Complete a full shutdown by pressing the start button, and choose the Shut Down option. Unplug your router from the power outlet for a full 30 seconds. This allows the router to completely reset its memory and clear any temporary glitches. Plug it back in, wait for it to fully boot up (usually indicated by solid lights), and then power on your Windows 7 system. Frequently, this simple task resolves many connectivity problems.
Step 2: Diagnosing and Repairing Network Adapter Issues – The Driver's Role
The network adapter driver is the software that allows your computer to communicate with your WiFi network. Outdated, corrupted, or incompatible drivers are common culprits behind connectivity issues. Here's how to check and, if necessary, update or reinstall your network adapter driver:
- Accessing Device Manager: Click the Windows Start button, type "Device Manager" into the search bar, and press Enter. This opens the Device Manager, a central repository of all your computer's hardware.
- Locating Network Adapters: In Device Manager, expand the "Network adapters" category. You’ll see a list of your network adapters, including your WiFi adapter (it might be labeled something like "Wireless Network Adapter" or "WiFi Adapter").
- Checking for Errors: Look for any yellow exclamation marks or red crosses next to your WiFi adapter. These indicate a problem with the driver.
- Updating the Driver: Right-click your WiFi adapter, and select "Update driver software". Choose "Search automatically for updated driver software." Windows will attempt to find and install the latest driver. If successful, restart your computer.
- Reinstalling the Driver: If updating doesn't work, right-click your WiFi adapter again and select "Uninstall". When prompted, confirm the uninstall. Then, restart your computer. Windows should automatically reinstall the driver. If not, visit the manufacturer's website (e.g., Intel, Realtek, Broadcom) and download the latest driver for your specific WiFi adapter model, making sure it is compatible with Windows 7.
- Rolling Back the Driver: If a recent driver update caused the problem, right-click the adapter, select "Properties," go to the "Driver" tab, and, if available, click "Roll Back Driver." This will revert to the previous version.
Step 3: Examining Your Network Settings and Connections
Incorrect network settings are another common problem. Ensure your settings are correctly configured to connect to your WiFi network.
- Accessing Network and Sharing Center: Click the network icon in the system tray (lower right corner of your screen). If you have a WiFi connection you should find a diagram of computers and the internet. Click "Open Network and Sharing Center."
- Checking Wireless Network Connection Status: In the Network and Sharing Center, click "Change adapter settings" on the left side. Right-click your wireless network connection (it will have a WiFi signal icon) and select "Status."
- Verifying IP Address and DNS Settings: In the Wireless Network Connection Status window, click "Details." Ensure that both the IP address and DNS server addresses are valid and that the connection status is "Connected."
- Configuring TCP/IP Settings (If Necessary): Right-click your wireless network connection in "Change adapter settings" and choose "Properties." In the properties window, select "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)" and click "Properties." Ensure that "Obtain an IP address automatically" and "Obtain DNS server address automatically" are selected. If you have a specific IP address or DNS settings, make sure they're correctly entered, or that your router supports them.
Step 4: Troubleshooting Router-Related Issues: The Heart of the Network
Your router plays a vital role in your WiFi connectivity. Sometimes, the problem lies not with your computer, but with the router itself.
- Restarting the Router: As mentioned in Step 1, restarting your router is a quick fix that can resolve many issues.
- Checking the Router's Firmware: Router firmware is the software that runs the router. Outdated firmware can cause various problems, including WiFi connectivity issues. Check your router manufacturer's website for firmware updates. Follow the manufacturer's instructions to update the firmware.
- Changing the WiFi Channel: WiFi routers broadcast on different channels. In crowded environments, multiple routers broadcasting on the same channel can cause interference. Log in to your router's configuration page (usually by typing the router's IP address into your web browser, like 192.168.1.1, often found on a sticker on the router). Look for the "Wireless Settings" or "WiFi Settings" and change the channel to 1, 6, or 11. These channels are less prone to interference. Save the settings and restart the router.
- Checking the Router's Security Settings: Ensure your router is using a secure wireless security protocol (e.g., WPA2 or WPA3). Avoid using outdated protocols like WEP, which are easily compromised. If using WPA2 or WPA3, ensure you’re using a strong password.
Step 5: Minimizing Interference – Creating an Optimal WiFi Environment
WiFi signals can be easily disrupted by interference from other devices, which might be a primary reason for a poor connection.
- Identify Potential Sources of Interference: Common culprits include microwave ovens, Bluetooth devices, cordless phones (especially older ones operating at 2.4 GHz), and other electronic devices emitting radio waves.
- Relocate Your Router: Move your router away from potential sources of interference, ideally to a central location in your home or office. Keep it elevated and away from walls or metal objects that might obstruct the signal.
- Consider Using the 5 GHz Band (If Applicable): Many modern routers broadcast on both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. The 5 GHz band offers faster speeds and is less prone to interference, but has a shorter range. If your devices support 5 GHz, connect to that network instead.
Step 6: Run the Windows Network Troubleshooter – a Built-in Solution
Windows 7 has a built-in network troubleshooter that can automatically diagnose and fix common network problems.
- Accessing the Troubleshooter: Right-click the network icon in the system tray (lower right corner of your screen) and select "Troubleshoot problems."
- Following the Prompts: The troubleshooter will scan for problems and, if possible, automatically fix them. Follow the on-screen prompts. This is an incredibly valuable resource for resolving fundamental connection problems.
Step 7: Resetting TCP/IP and Winsock – Clean Slates for the Network
Sometimes, the network settings can become corrupted at a deeper level. Resetting TCP/IP and Winsock is a more advanced troubleshooting step that can often resolve stubborn networking problems.
Opening the Command Prompt: Click the Windows Start button, type "cmd" in the search bar, right-click "Command Prompt," and select "Run as administrator." You need administrator privileges to run these commands.
Executing the Commands: In the Command Prompt window, type the following commands, one at a time, pressing Enter after each:
netsh winsock resetnetsh int ip reset
Restarting Your Computer: After executing these commands, restart your computer. This process will reset the TCP/IP stack and Winsock catalog to their default settings.
Step 8: Checking for Malware – Protect Your WiFi Connection
Sometimes, malware can interfere with your network connection. Regularly scan your system for malware and remove any detected threats. Ensure that your antivirus software is up-to-date and that you've run a full system scan. Malware can hijack your network settings or consume bandwidth, leading to slow or unreliable WiFi performance.
Going Beyond the Minute: Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
While the above steps often resolve WiFi problems within a minute, some scenarios require a deeper
